Materials Science
Advanced wound dressings
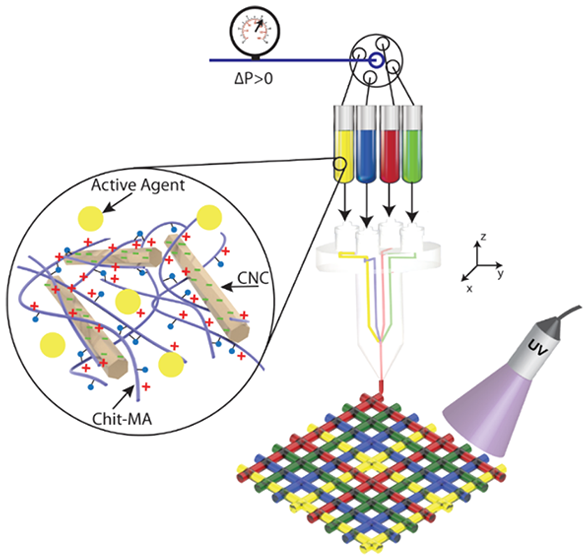
Advanced wound dressings improve wound healing by releasing antibacterial agents, accelerating wound closure, and reporting changes in the wound's state. We are developing 3D printed programmable multicomponent hydrogel wound dressings that selectively (site-specifically) release ions, small molecules, metal nanoparticles, and proteins for enhanced wound healing. We are also interested in antibacterial wound dressings that sequester of ions and molecules much needed by bacteria, thus depriving bacteria growth in wounds.
Representative publications
Alizadehgiashi, M. et al. Multifunctional 3D printed wound dressings. ACS Nano 15, 7, 12375 (2021)
Chekini, M. et al. Nanocolloidal hydrogel with sensing and antibacterial activities governed by iron ion sequestration. Chem. Mater. 32, 10066 (2020)
Nanocolloidal inks for 3D printing

We conceptualize and synthesize nanoparticle-based inks for 3D printing. Such inks, in addition, to the functionality provided by nanoparticles, have highly beneficial rheological properties such as shear thinning and self-healing.
Representative publications
Morozova, S. M. et al. Multicolored nanocolloidal hydrogel inks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2105470 (2021)
Khuu, N. et al. Temperature-mediated microfluidic extrusion of structurally anisotropic hydrogels. Adv. Mater. Technol. 4, 1800627 (2019)
Khabibullin, A. et al. Injectable shear-thinning fluorescent hydrogel formed by cellulose nanocrystals and graphene quantum dots. Langmuir 33, 12344 (2017)
Actuating materials for soft robotics

We conceptualize, design, and synthesize polymer materials that undergo shape change in response to external stimulus. and have applications in soft robotics, drug delivery, sensing, and cell culture. Actuation occurs due to differential materials’s response to the stimulus and is achieved by modulating its composition or structural anisotropy.
Representative publications
Gevorkian, A. et al. Actuation of 3D-printed Nanocolloidal Hydrogel with Structural Anisotropy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2010743 (2021)
Li, Y. et al. Supramolecular nanofibrillar thermoreversible hydrogel for growth and release of cancer spheroids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 6083-6087 (2017)
Wu, Z. L. et al. Three-dimensional shape transformations of hydrogel sheets induced by small-scale modulation of internal stresses. Nat. Comm. 4, 1586 (2013)
Ion sequestration for water purification

We are interested in hydrogels that selectively uptake heavy metal ions from water. Currently, we have demonstrated high scavenging capacity for Hg2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Ag+ ions for hydrogels that have a large surface area and abundance of ion-coordinating sites.
Representative publications
Alizadehgiashi, M. et al. Nanocolloidal hydrogels for metal ion scavenging. ACS Nano 12, 8160 (2018)